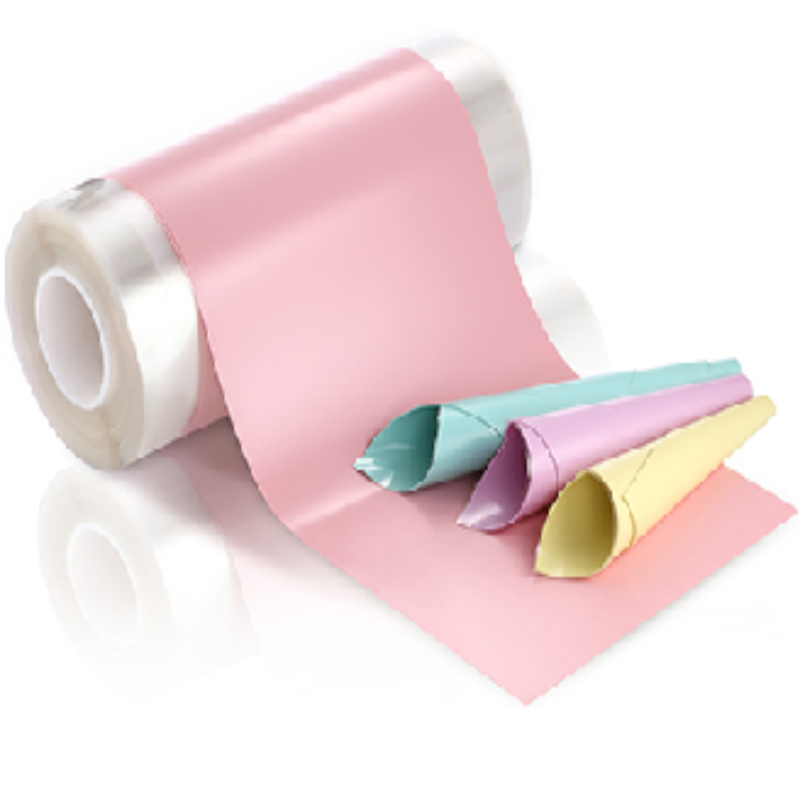
Non-silicone thermally conductive pads
No silicone volatile material in the material, also known as no oil permeation and pollution-free Nthermally conductive silicone pads for silicone-sensitive applications, lower hardness than traditional non-silicone materials, providing higher deformation with higher thermal conductivity
Silicone-free thermally conductive silicone uses a silicone-free compound as the base material, avoiding the volatiles that may be produced by silicone in high temperature environments and further improving thermal conductivity.
Compared with traditional silicone, silicone-free thermally conductive silicone has a higher thermal conductivity, which can effectively transfer heat to heat sinks or other heat dissipation devices and improve the heat dissipation efficiency of the devices.
-Available thermal conductivity range : 1W~6W
-Available specifications: sheet, slice, punch, backing (can be die-cut into various sizes and shapes according to customer’s specification).
-Thickness: Thickness range: 0.5~5mm Conventional thickness generally: 0.5mm, 0.75mm, 1.0mm, 2.0mm, etc.
-Hardness: Shore C 20~45, special hardness can be customised according to requirements
Netcom products, 5G base stations, high frequency modules, communication equipment, artificial intelligence, consumer electronics, aerospace, medical equipment, etc.




Get A Free Quote
ShenZhen Great Technoloy Co., Ltd. was founded in 2005, specializing in the research and development, production and sales of silicone and rubber products.
Related products
Low Siloxane Overflow Thermal Pad
It is a kind of thermal interface material with ultra-low hardness, ultra-low heat, and ultra-low oil emission.
EMI Thermal Conductive Silicone Pad
Netcom products, 5G base stations, high frequency modules, communication equipment, artificial intelligence, consumer electronics, aerospace, medical equipment, etc.
Thermal Pad
Thermally conductive silicone pad is a thermally conductive medium material synthesised through a special process using silicone as the base material and adding various auxiliary materials such as metal oxides.